Exploring the Citrine Crystal Cluster: An In-Depth Analysis


Intro
Citrine crystal clusters have fascinated collectors and enthusiasts for generations. Their vibrant yellow to golden hues are not only visually striking but are also steeped in rich geological history. This article will provide an in-depth look into various aspects of citrine crystal clusters. From their formation to their practical applications, we will explore the many dimensions that make citrine significant in both natural and metaphysical contexts.
Rock and Fossil Identification
While the focus is primarily on citrine, understanding how to identify various crystal types enhances one's appreciation of these geological formations. Key aspects of identification include:
- Types of rocks: Citrine is a variety of quartz, often confused with other crystal forms like amethyst or smoky quartz. Knowing the physical traits of these crystals will aid in differentiation.
- Characteristics to look for: Clarity, color intensity, and shape are critical in identifying citrine. Look for well-defined points and a lack of inclusions to determine quality.
- Tools for identification: A magnifying glass or jeweler's loupe can help in examining details. Additionally, a refractometer can measure the refractive index, confirming the presence of citrine.
Collecting Tips and Techniques
For those interested in adding citrine crystal clusters to their collection, certain best practices can enhance the experience:
- Best practices for collecting: Always research the source and authenticity of the crystals. Ensure that they are ethically sourced and responsibly harvested.
- Locating prime collecting sites: Seek out areas known for their geological formations. Locations in Brazil and Madagascar are renowned for yielding high-quality citrine.
- How to safely extract specimens: Use proper tools to avoid damaging the crystals or surrounding environment. Wear gloves to prevent oils from your skin from affecting the specimen and ensure you follow local regulations.
Preservation and Display
Once collected, proper preservation and display methods prolong the life of citrine crystal clusters:
- Techniques for preserving rocks and fossils: Keep crystals away from direct sunlight to prevent fading. Regular cleaning using a soft brush can also help maintain their luster.
- Proper storage methods: Store in a padded box or case to prevent scratching. Avoid placing too many crystals in the same container as they may chip each other.
- Creative display ideas: Consider using display stands or shadow boxes. Lighting can also enhance the beauty of citrine, making it a focal point in any room.
Geological Insights
Understanding citrine from a geological perspective enriches the appreciation of this crystal:
- Geological formations and processes: Citrine forms through a combination of volcanic activity and hydrothermal processes. Understanding these methods provides insight into its rarity and composition.
- Historical significance of rocks and fossils: Citrine has been valued since ancient times for both its beauty and alleged metaphysical properties. It has appeared in jewelry and decor throughout history.
- Notable discoveries in the field: Significant finds, particularly in Brazil, have highlighted the potential for high-quality citrine. These discoveries shape the market and influence collecting trends.
"Citrine is often associated with wealth and prosperity, which adds a cultural layer to its geological significance."
In sum, this analysis of citrine crystal clusters will equip collectors with knowledge and appreciation for these incredible natural wonders. Dive into this unique aspect of geology and embrace the beauty and significance of citrine.
Prologue to Citrine Crystal Clusters
Citrine crystal clusters hold a unique place in both geological study and the collectible market. Their beauty and perceived metaphysical properties attract a diverse audience, from rock enthusiasts to spiritual seekers. Understanding citrine is essential for recognizing its significance in various contexts, including both natural formations and human usage. This introduction sets the stage for an in-depth exploration of citrine crystal clusters, their distinctive features, and the relevance they have in today’s society.
Definition and Basic Characteristics
Citrine is a variety of quartz that ranges in color from pale yellow to brownish orange. The name itself originates from the French word "citron," meaning lemon, reflecting its typical yellow hue. Citrine is transparent and displays a vitreous luster. A notable feature of citrine crystals is their ability to form in clusters or geodes, which can exhibit many individual crystal points radiating from a central base. This structure not only enhances their aesthetic appeal but also plays a role in their energy properties, often considered by those interested in metaphysics.
When evaluating citrine clusters, collectors should consider color richness, clarity, and size. The characteristics mentioned often dictate the desirability and value of the crystal. Smaller, well-formed clusters may attract attention for their intricate structures, while larger specimens are valued for their presence and overall visual impact.
Geological Origins
The geological origins of citrine are rooted deeply in mineral formation processes. Most natural citrine forms from amethyst or smoky quartz through specific geological conditions. Heat plays a pivotal role; natural citrine typically originates from regions abundant in iron. When amethyst is subjected to heat, the iron content oxidizes, leading to yellow hues. This suggests that the citrine comes from alterations of existing crystals rather than standalone formations.
Brazil and Madagascar are two significant sources of citrine, providing some of the most sought-after specimens in the market. The geological activity in these areas has facilitated the formation of striking citrine clusters, which collectors value highly. Additionally, synthetic processes have introduced heat-treated alternatives, which resemble natural citrine but are created in controlled environments. Yet, the natural formations maintain an allure due to their unique geological history.
"Understanding the geological roots of citrine not only informs collectors but also enriches the appreciation of this beautiful mineral."
The Formation of Citrine
Understanding the formation of citrine is essential to appreciate its unique properties. This process encompasses several geological and chemical elements that shape the crystal's characteristics. Knowing these aspects allows collectors to identify genuine citrine and determine its value.
Mineral Composition
Citrine is primarily composed of silicon dioxide, which is the same basic material as most quartz varieties. The trace amount of iron within the crystal is what provides its distinct yellow to orange hue. Fe2O3 is responsible for this coloration. This unique mineral composition contributes to citrine's durability, making it advisable for collectors who prioritize both aesthetic and functional qualities in their specimens.
Also, the concentration of iron varies. Higher levels can result in deeper shades, while lower levels yield paler colors. Recognizing these subtle differences can influence pricing and desirability among collectors. Environmental factors, such as heat and pressure, during crystallization also play a critical role in determining the final composition of the citrine found in nature.
Crystallization Process


The crystallization of citrine follows a meticulous process. This begins in hydrothermal environments, where hot mineral-rich water permeates through the Earth’s crust. As pressure and temperature fluctuate over geological time, silicon dioxide in dissolved form crystallizes. Typically, this occurs slowly, allowing for the formation of large and well-defined crystals.
In the case of citrine, the presence of iron during this crystallization is crucial. Warm temperatures facilitate iron in achieving its solubility, eventually leading to the formation of citrine rather than amethyst, which also originates from the same mineral. Thus, understanding the crystallization process enriches the knowledge of the conditions under which citrine forms and ultimately helps collectors assess authenticity and value.
Natural vs. Heat-Treated Citrine
Citrine exists in two primary forms: natural and heat-treated variants. Natural citrine is relatively rare, making it more sought after by collectors. Formation occurs over thousands of years in specific geological conditions without human interference. However, most of the citrine available in the market is heat-treated amethyst. This process involves exposing amethyst to high temperatures, resulting in a color change that transforms it into citrine.
The differentiation between natural and heat-treated citrine is vital for collectors. Heat-treated versions typically exhibit lighter shades of yellow and may lack the deeper hues found in natural specimens. Therefore, discerning between these two types impacts value, as natural citrine commands a higher price due to its rarity.
Characteristics of Citrine Crystal Clusters
Citrine crystal clusters are notable for their unique attributes that set them apart from other gemstones. Understanding the specifics of citrine's characteristics is essential for both collectors and enthusiasts. The beauty and rarity of citrine lie in its colors, clarity, and diverse shapes. Each of these elements not only enhances its aesthetic appeal but also influences its value and significance in various contexts.
Color Variations
The color of citrine ranges from pale yellow to deep amber. The hue is a result of the presence of iron within the crystal structure. Pale shades often suggest a lighter energy, appealing to those seeking subtlety in their collections. Deeper colors, such as orange and brown, are generally more sought after, indicating a richer vibrational frequency. This variability allows for personalization in selection and can align with different metaphysical beliefs. For instance:
- Light Yellow: Associated with clarity and optimism.
- Golden Brown: Linked to abundance and prosperity.
- Dark Amber: Most potent in energy alignment.
These colors are often what attract potential collectors and can significantly impact the crystal's market value.
Clarity and Transparency
The clarity of citrine is a crucial characteristic that must be considered. High-quality citrine showcases minimal inclusions, resulting in greater transparency. Crystals that are flawless or have very few visible blemishes command a premium price. Such clarity not only enhances the visual beauty but also contributes to the crystal’s perceived energy. A transparent citrine is often believed to have stronger vibrational frequencies. Collectors should be aware of the grading of citrine:
- Flawless: Completely clear; highly valued.
- Slightly Included: Minor inclusions that are only noticeable under magnification.
- Included: Significant blemishes that affect overall appearance and value.
Recognizing these traits is vital for assessments in sustainability and value preservation.
Size and Shape Diversity
Citrine crystal clusters vary widely in size and shapes. This diversity allows collectors a broad spectrum of options for display and use.
- Small Clusters: Often used in jewelry, easily incorporating into designs.
- Medium-Sized Pieces: Ideal for decor or energy work spaces.
- Large Clusters: Serve as statement pieces, often used in holistic healing centers.
Shapes can range from pointed formations to more rounded structures, each believed to radiate energy differently. Pointed clusters are thought to direct energy, while rounded clusters may disperse it. This makes selecting the right shape critical for intended use. Enthusiasts may find satisfaction in the challenge of identifying the specific characteristics that resonate with their individual needs and aesthetic preferences.
Citrine in Historical Context
Citrine crystal clusters possess a rich historical backdrop that intertwines with human culture and beliefs. Their presence in various civilizations underscores their importance in art, spirituality, and practical uses. Understanding the historical context of citrine enhances its value and relevance today, particularly for collectors and enthusiasts. This section examines how ancient civilizations utilized citrine and the evolving symbolism associated with this striking gemstone.
Usage in Ancient Civilizations
Citrine has been revered since ancient times. Its striking hues of yellow and gold captured the attention of many cultures across the globe. Records indicate that the ancient Egyptians used citrine not just for adornment but also in talismans and amulets. They believed that citrine offered protection and absorbed negative energy, making it a prized possession in burial sites and tomb artifacts. The Greek and Roman cultures similarly recognized the crystal's beauty. They made jewelry and decorative objects, showcasing the brilliance of citrine. It was believed to bring prosperity and success, adding to its desirability.
In China, citrine was associated with wealth and prosperity. Merchants often carried citrine with them as a good luck charm, hoping to attract fortune during trading ventures. The synergy between trade and the crystal's reputation further cemented its place in commerce. Throughout these ancient societies, citrine was not merely ornamental; it served a significant role in cultural practices and beliefs.
Symbolism Through Time
Over the centuries, the symbolism of citrine has undergone various transformations. Initially, its vibrant colors represented vitality and health, which were essential attributes to many cultures. The sunny aspects of citrine symbolized warmth and abundance. For instance, in the Middle Ages, citrine was believed to purify the spirit and bring clarity of thought. It was sometimes called the "merchant's stone" due to its association with prosperity and well-being.
In more contemporary times, citrine's symbolism has expanded to encompass attributes like creativity and emotional balance. It is often regarded as a healing stone, believed to impart positive energy and motivation. Additionally, citrine is recognized for its connection to the solar plexus chakra, which governs personal power and self-confidence.
This shift in perception highlights how citrine has transcended its initial uses, becoming influential in both spiritual and wellness communities today. Its historical significance lays a foundational understanding for modern collectors, offering insight into the crystal's multi-dimensional character.
Citrine, with its luminous hues, serves not only as a gemstone but also as a testament to humanity's deep relationship with nature and its elements.
Metaphysical and Healing Properties
The metaphysical and healing properties of citrine crystal clusters play a significant role in the allure and value of these stones. Many collectors and enthusiasts are drawn to citrine not only for its aesthetic appeal but also for the purported benefits associated with its energy. Understanding these properties allows individuals to appreciate the deeper dimensions of citrine beyond its geological composition.
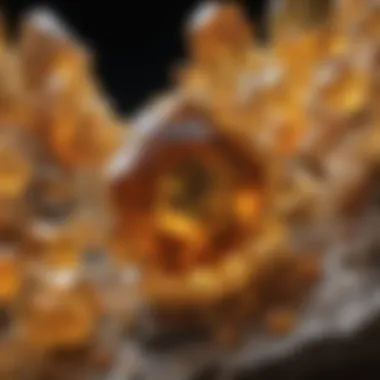

Spiritual Significance
Citrine is often associated with spiritual elevation and personal empowerment. Known as the "merchant's stone", it is believed to attract abundance and prosperity. Many find that carrying or meditating with citrine helps to establish a positive mindset and enhances creativity. The stone is often linked with the solar plexus chakra, which governs personal power, will, and self-confidence.
- It promotes self-expression and discourages fear of confrontation.
- Many users report a deeper connection to their inner self when working with this stone.
- Its uplifting energy is said to help dispel negative feelings, inspiring joy and optimism.
"Citrine has been revered for its ability to energize, while bringing clarity to the thoughts and intentions of the user."
Energy Work and Chakras
When incorporated into energy work, citrine serves as a powerful tool for activating and balancing chakras. Practitioners often use it in conjunction with meditation or crystal healing techniques. The connection between citrine and the solar plexus chakra is particularly notable, as this chakra is essential for personal power and self-esteem. It influences factors such as confidence and control over one’s life.
- Chakra Alignment: To work effectively with citrine, one may consider placing it on the solar plexus area during meditation. This can enhance the flow of energy through this center, facilitating personal growth.
- Energy Flow: Citrine is thought to help enhance the flow of positive energy throughout the body while cleansing and rejuvenating the aura.
In sum, the spiritual significance and energy properties of citrine crystal clusters make them more than just decorative objects. They symbolize empowerment and positive transformation, appealing to collectors interested in the metaphysical aspects of these crystals.
Caring for Your Citrine Crystal Cluster
Caring for your citrine crystal cluster is vital for maintaining its beauty and sustaining its energy properties. Proper care ensures that the cluster remains vibrant and effective, particularly for those who use it in metaphysical practices. Not only does it enhance the aesthetic appeal, but it also helps in preserving the unique qualities of the citrine crystal.
Cleaning Techniques
Cleaning your citrine crystal cluster should be approached delicately. Here are recommended techniques to maintain its clarity and sheen:
- Water and Soft Cloth: Use lukewarm water. Gently wipe with a soft cloth to remove dust or residue. Avoid abrasive materials, as they can scratch the surface.
- Saltwater Solution: Some collectors prefer to submerge their citrine in a saltwater solution for a few hours. This method is thought to cleanse away negative energy. After immersion, rinse the cluster thoroughly and dry it with a soft towel.
- Sound Cleansing: A more unconventional method involves using sound frequency, such as a singing bowl. The vibrations can help clear any stagnant energy while ensuring the cluster’s physical integrity remains intact.
- Drying Methods: Allow the cluster to dry naturally in a safe place. Avoid direct sunlight to prevent fading.
Important Note: Always test any cleaning method on a small or less visible part of the cluster first.
Storage Recommendations
Proper storage is necessary to protect citrine crystal clusters from damage and to ensure they retain their energetic properties. Consider these suggestions:
- Use Soft Cases or Pouches: Store individual clusters in soft cases or padded velvet pouches to prevent scratching and damage.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Keep the clusters in a temperature-controlled environment. Extreme heat or cold can affect their structure and energy properties.
- Separate from Other Crystals: Store citrine away from other crystals, especially harder stones, to avoid scratches. Different crystals can have varying chemical properties that might adversely affect one another.
- Display Wisely: If used for decoration, find a stable and firm surface. Ensure that the area is dimly lit to prevent prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
By implementing these care techniques and following proper storage guidelines, you can ensure that your citrine crystal cluster maintains its integrity while also enhancing its benefits. Care is not just about keeping it clean; it is about respecting and preserving the natural properties inherent in these beautiful geological formations.
Collecting Citrine Crystal Clusters
Collecting citrine crystal clusters can be a rewarding endeavor for both enthusiasts and serious collectors alike. These stunning formations not only serve as decorative pieces but also offer various physical and metaphysical benefits. Whether you are new to collecting or consider yourself an aficionado, understanding how to properly collect citrine is crucial. The focus should be on several elements: authenticity, purchase sources, and pricing strategies. Each of these components influences not just the enjoyment of your collection but also its potential value.
Identifying Authenticity
The importance of identifying authenticity in citrine crystals cannot be overstated. With various treatments and synthetic alternatives available in the market, it is essential to distinguish genuine citrine from imitations. Authentic citrine typically exhibits a rich amber color, often with a transparent yet slightly smoky appearance. To verify authenticity, collectors should look for several features:
- Color Consistency: Real citrine usually has a uniform color.
- Inclusions: Natural formations may have minor inclusions or imperfections.
- Glass Tests: Some methods, such as checking for thermal conductivity, can help ascertain if the piece is genuine.
Be cautious of overly bright and uniform pieces, as these are often signs of heat-treated amethyst rather than true citrine. As a rule of thumb, when in doubt, seek specialization and consult credible sources for verification.
Where to Buy
Finding high-quality citrine crystal clusters requires a discerning approach. Several avenues exist for acquiring these formations, each with its own pros and cons:
- Gem Shows: These events offer a wide variety and the opportunity to interact directly with sellers. It is an effective way to assess quality through direct inspection.
- Specialty Crystal Shops: Local shops often carry authentic specimens and can provide insights into various crystals.
- Online Retailers: Platforms such as eBay or Etsy can have a vast selection, but careful evaluation of seller ratings and product descriptions is vital.
- Mineral Expos and Auctions: These can be great avenues for finding unique or rare pieces.
Research local events or online communities can also lead to finding reputable sources. Membership in rock and mineral societies may grant additional access to buying opportunities.
Pricing Factors
When it comes to pricing, several factors influence the cost of citrine crystal clusters. Understanding these factors can ensure you make informed decisions, whether you’re investing or simply collecting:
- Size and Clarity: Larger, clearer specimens typically command higher prices due to their rarity.
- Color Saturation: Deeper, more vibrant colors often have a higher value, while pale or washed-out colors may be less desirable.
- Condition: Chipped or damaged crystals usually see a price reduction, while well-preserved pieces maintain their value.
- Provenance: Crystals with a verified history or unique origins may fetch higher prices.

In summary, collecting citrine crystal clusters is not just about acquiring beautiful specimens; it’s a meticulous process that involves knowing how to identify authenticity, finding reputable places to buy, and understanding pricing dynamics. With proper knowledge and care, your collection can flourish, while also serving as an investment.
Citrine in Modern Culture
Citrine has emerged as a prominent player in contemporary culture, finding its niche not only among collectors and esoteric enthusiasts, but also within modern fashion and wellness communities. Its vibrant yellow hues evoke feelings of cheerfulness and vitality, making it a favored choice in various spheres, from interior design to personal adornments. This segment analyzes the specific trends surrounding citrine, as well as its applications in jewelry making, offering insights into its growing popularity and cultural significance.
Popular Trends
The rise of citrine in modern culture aligns with broader trends of naturalism and holistic wellness. Many consumers are increasingly drawn to natural stones due to their purported healing properties and aesthetic appeal. Citrine, in particular, captures attention for several key reasons:
- Aesthetic Appeal: The warm yellow tones of citrine make it an attractive choice for home decor. Its ability to blend with various color palettes enhances its desirability.
- Wellness Trend: There is a growing interest in crystals as tools for meditation, energy healing, and self-care. Citrine is often associated with positive energy and creativity, making it a popular choice among wellness practitioners.
- Sustainable Sourcing: As sustainability becomes more integral to consumer choices, ethically sourced citrine appeals to conscious buyers. Collectors and enthusiasts look for materials that reflect their values, increasing the demand for responsibly mined crystals.
Citrine in Jewelry Making
Citrine's unique properties and aesthetic qualities have led to its incorporation into various jewelry styles. This includes everything from elegant necklaces to statement rings. Jewelers and designers favor citrine for several reasons:
- Versatility: Citrine adapts well to both classic and modern designs. Its vibrant color can complement various gemstones, elevating overall design.
- Affordability: Compared to other gemstones, citrine is often more affordable, allowing a broader audience access to quality jewelry without the premium cost of diamonds or sapphires.
- Symbolism: Citrine represents clarity, positivity, and abundance. Its inclusion in jewelry not only enhances its aesthetic value but also resonates with those seeking to promote specific ideals in their lives.
"Citrine is not just a beautiful gemstone; it embodies the warmth and vitality that many of us seek in today’s complex world."
End
Citrine crystal clusters have found their place in modern culture, from enhancing personal style through jewelry to enriching living spaces with positive energy. The ongoing interest in natural stones, along with rising trends in ethical consumption and wellness, underscores the significance of citrine in contemporary society. As its popularity continues to rise, citrine remains a lasting symbol of beauty, positivity, and connection to the earth.
Conservation and Ethics in Collecting
Collecting citrine crystal clusters presents both opportunities and responsibilities. As interest in these unique geological formations increases, so does the importance of ethical considerations in their acquisition and conservation.
Sustainable practices are crucial for ensuring that collectors contribute positively to the environment and local communities. The mining of citrine, like many natural resources, can have detrimental effects on ecosystems. Unregulated mining operations can lead to habitat destruction, water pollution, and adverse social effects on local populations. Therefore, collectors should seek to acquire citrine from sustainable sources. This includes mining companies that prioritize environmentally-friendly practices, such as land reclamation and minimal environmental impact. Supporting ethical miners not only protects the environment but also ensures that local workers are treated fairly.
Sustainable Practices
Practicing sustainability in collecting does not require extensive knowledge. However, being aware of where and how citrine is sourced is a significant first step. Here are some recommended sustainable practices:
- Research Suppliers: Use suppliers who clearly state their sourcing practices. Companies involved in responsible mining will often highlight their commitment to sustainability on their websites.
- Opt for Second-Hand Stones: Buying used citrine reduces the demand for new mining operations. This practice also aids in recycling existing materials.
- Advocate for Certification: Support organizations that certify sustainable practices in mining. Familiarize yourself with certification logos to ensure products meet ethical standards.
By utilizing these practices, collectors can contribute to a healthier planet and a more equitable market.
Legal Aspects of Collecting
In addition to ethical considerations, understanding the legal framework surrounding citrine collection is essential. Laws vary widely depending on the country and region, making it crucial for collectors to educate themselves on local regulations. Some countries have strict laws governing the collection of minerals, protecting certain species or even entire areas from harvesting.
It is also important to be aware of international trade laws. For example, citrine sourced from specific locations may have export restrictions that must be adhered to. Collectors should be attentive to certifications that demonstrate the legality of their purchases.
"Engaging with the law around collecting is as critical as the collection itself. Know your rights and responsibilities as a collector."
Additionally, being part of a collector community can be beneficial. Members of organizations dedicated to mineral collecting are often aware of legal updates and best practices, which can help collectors navigate the complex legal landscape. Joining forums or attending workshops can provide valuable resources for those looking to expand their knowledge.
In summary, conservation and ethics in collecting citrine crystal clusters shape not just individual practices, but also the broader narrative of how we interact with our natural resources. By understanding sustainable practices and legal aspects, collectors can ensure that their passion aligns with responsibility.
End and Future Directions
The conclusion section is pivotal for encapsulating the essence of this article on citrine crystal clusters. It serves as a reflection on the various facets covered, such as the geological formation, unique characteristics, and cultural significance of citrine. This part also emphasizes the importance of understanding the ethical implications surrounding the collection and conservation of these natural treasures. As the world increasingly acknowledges the need for sustainable practices, an awareness of environmental impact and legality in collecting becomes essential.
Importance of Conclusion and Future Directions:
The conclusion not only summarizes key insights but also lays the groundwork for future exploration. It encourages collectors and enthusiasts to engage with citrine in a conscientious manner, promoting education around sourcing and preserving these crystals.
Summary of Main Points
In this article, we have explored numerous aspects of citrine crystal clusters:
- Geological Origins: Understanding how citrine forms helps in appreciating its natural beauty and diversity.
- Characteristics: Details about color, clarity, and shape offer critical insights for collectors.
- Historical and Cultural Context: Showcasing its significance in ancient civilizations and symbolic meanings.
- Metaphysical Properties: Discussing the spiritual significance attributed to citrine enhances its appeal in alternative healing practices.
- Care and Conservation: Proper treatment and storage of citrine ensure its longevity for future generations.
- Ethics in Collecting: Emphasizing sustainable and legal practices in the acquisition of citrine reinforces responsible collecting.
By summarizing these key points, the reader gains a comprehensive understanding of why citrine crystal clusters deserve respect and careful consideration in both collection and enjoyment.
Future of Citrine Collection
The future of citrine collection looks promising yet requires thoughtful action.
- Awareness of Sustainability: As environmental issues gain traction, collectors must prioritize sourcing crystals responsibly. Choosing to purchase from ethical suppliers supports conservation efforts.
- Education on Authentication: As demand grows, so do counterfeit goods. Future collectors need to be educated on how to identify genuine citrine to avoid exploitation.
- Integration in Design: Citrine's appeal continues to rise in jewelry making and home decor. Its vibrant color complements modern aesthetics, making it a versatile choice for both collectors and designers.
- Community and Networking: Online platforms, such as Reddit, foster a sense of community among collectors. These spaces provide valuable information on trends, techniques, and ethical sourcing.
- Research and Innovation: Ongoing studies into the properties and origins of citrine can yield novel insights, pushing the boundaries of gemology and collection methods.







